Tensor Processing Units (TPUs): The Core Engine Behind Gemini AI
Artificial intelligence has advanced rapidly over the last decade, and much of this progress comes not only from smart algorithms but from powerful hardware designed specifically for AI. One of the most important pieces of this hardware is the TPU – Tensor Processing Unit, developed by Google. Today, TPUs are the backbone that powers large AI models, including Google’s Gemini.
This article gives a complete, easy-to-understand explanation of TPUs: what they are, how they work, why they are different from CPUs and GPUs, and why Gemini depends on them.
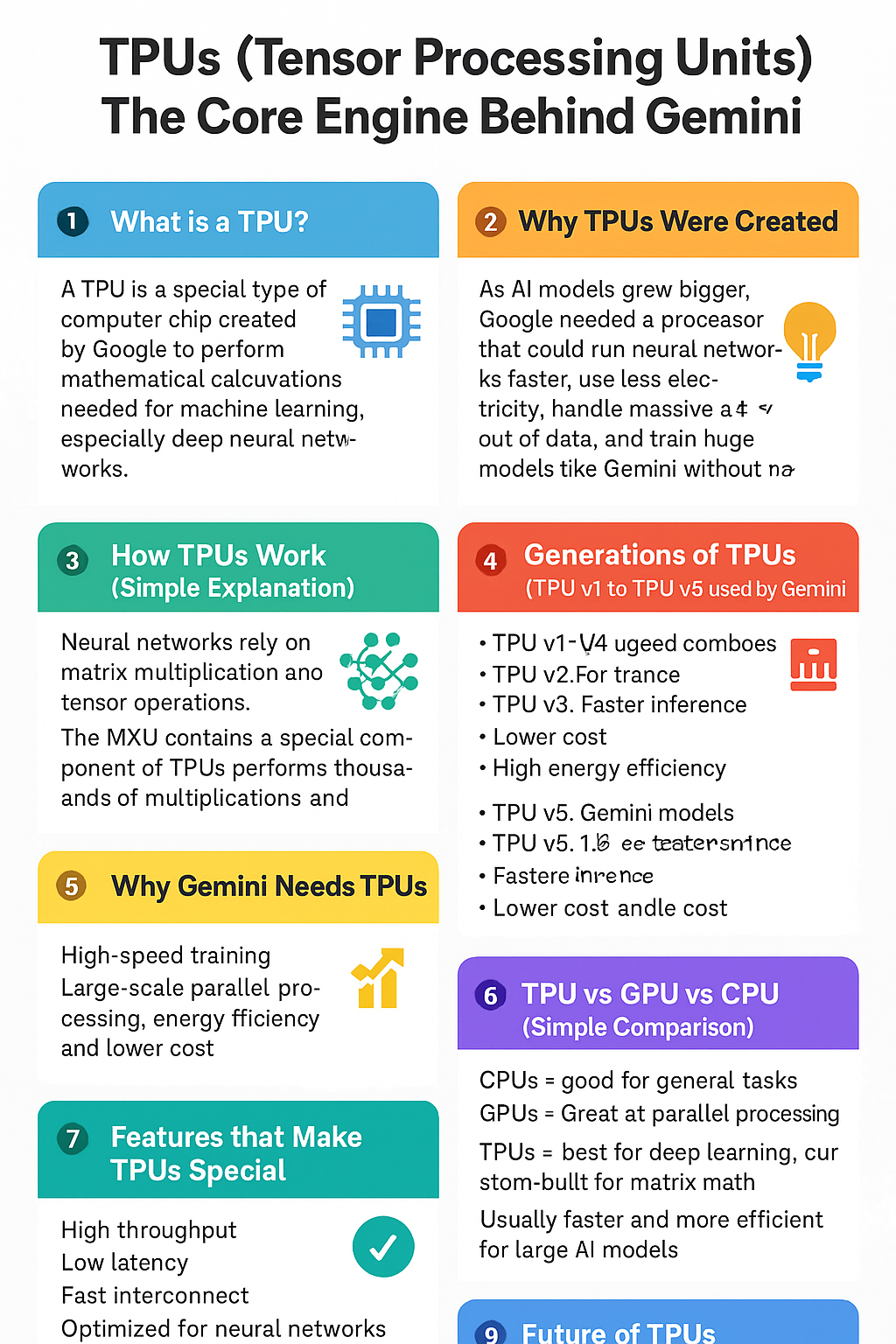
1. What is a TPU?
A Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) is a special type of computer chip created by Google to perform the mathematical calculations needed for machine learning, especially deep neural networks.
- “Tensor” refers to multi-dimensional arrays of numbers—the basic unit of data inside neural networks.
- “Processing Unit” means it handles calculations.
In simple words:
A TPU is a super-fast calculator built specifically for AI mathematics.
While CPUs (like your computer processor) and GPUs (used in gaming and some AI tasks) can run AI models, they are general-purpose. TPUs, however, are purpose-built, designed only for tensor math.
2. Why TPUs Were Created
As AI models grew bigger, Google needed a processor that could:
- Run neural networks faster
- Use less electricity
- Handle massive amounts of data
- Train huge models like Gemini without taking years
Traditional processors struggled with these demands. So Google engineered TPUs to directly accelerate the core math of machine learning: matrix multiplications.
3. How TPUs Work (Simple Explanation)
Neural networks rely on two main operations:
- Matrix multiplication
- Tensor (multi-dimensional) operations
These operations involve multiplying large grids of numbers over and over—millions or billions of times.
TPUs contain a special component called:
The MXU – Matrix Multiply Unit
- This unit performs thousands of multiplications and additions at the same time.
- It is massively parallel—meaning it can handle huge blocks of data together, not one piece at a time.
This is why TPUs are incredibly fast at running AI models.
4. Generations of TPUs (TPU v1 to TPU v5 used by Gemini)
Google has released several TPU versions. Each generation is more powerful and energy-efficient.
TPU v1
- Focused mainly on running (inference) AI models.
TPU v2
- Expanded for both training and inference
- Introduced support for floating point numbers (important for accuracy)
TPU v3
- Larger clusters
- Liquid cooling because of high heat output
TPU v4
- Used in Google Cloud AI
- Much faster communication between TPU chips
TPU v5 (used by Gemini models)
- The most powerful TPU generation currently available
- Built specifically to run massive foundation models like Gemini 1.0, 1.5, and 1.5 Flash
- Supports trillions of parameters
- Designed for:
- Faster training
- Faster inference
- Lower cost
- High energy efficiency
5. Why Gemini Needs TPUs
Gemini, Google’s latest family of AI models, is extremely large and complex. Models like Gemini 1.5 Pro have over 1 million context tokens and require enormous computation.
TPUs give Gemini:
1. High-speed training
Gemini models are trained on huge datasets such as:
- Text
- Images
- Audio
- Code
- Video
- Scientific data
Training these models needs billions of operations every second—TPUs are built exactly for this.
2. Large-scale parallel processing
TPUs can be connected in massive clusters known as TPU Pods, where thousands of chips work together. This lets Gemini train or respond faster than would be possible on GPUs alone.
3. Energy efficiency
TPUs use much less power than traditional hardware for the same AI workload.
4. Lower cost
Google designed TPUs to be affordable to run in the cloud. This reduces the cost of training and running large models like Gemini.
6. TPU vs GPU vs CPU (Simple Comparison)
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- Good for general tasks
- Flexible but slow for large AI models
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
- Great at parallel processing
- Used widely for AI
- Still general-purpose hardware
TPU (Tensor Processing Unit)
- Best for deep learning
- Custom-built for matrix math
- Usually faster and more efficient for large AI models
In practice:
- CPUs are like normal cars.
- GPUs are like sports cars.
- TPUs are like high-speed trains built specifically for one route.
7. Features that Make TPUs Special
✔ High throughput
TPUs process massive amounts of data in parallel.
✔ Low latency
Fast response times—important for real-time AI like Gemini Chat.
✔ Fast interconnect
TPUs are connected through high-speed links so they can communicate instantly.
✔ Optimized for neural networks
Every part of the chip is designed around tensor operations.
8. Where TPUs Are Used in the Real World
Besides powering Gemini, TPUs run:
- Google Search AI systems
- YouTube recommendations
- Google Photos recognition
- Google Translate
- Large-scale scientific simulations
- Cloud ML workloads for businesses
Any company using Google Cloud AI can also access TPUs.
9. Future of TPUs
Google is continuously improving TPU technology. Gemini’s future versions will rely on even more advanced TPUs capable of handling:
- Larger contexts
- Smarter reasoning
- Bigger multimodal models
- More efficient training
TPUs will remain one of the most important technologies in large-scale AI.
Conclusion
A TPU is a special processor created by Google to accelerate machine learning. It is extremely good at the mathematical operations required for neural networks. Because of their speed, efficiency, and scale, TPUs are essential for powering advanced AI systems like Google Gemini.


Be First to Comment