Executive Summary
AI data centers represent the next evolution in computing infrastructure, designed specifically to handle the massive computational requirements of artificial intelligence workloads. These facilities require specialized architecture, hardware, and operational approaches that differ significantly from traditional data centers. This article explores the critical building blocks necessary for successful AI data center implementation.
1. Physical Infrastructure Foundation
Site Selection and Design
The foundation of any AI data center begins with strategic site selection. Key considerations include proximity to power grids, fiber optic networks, and cooling resources. AI workloads generate significantly more heat than traditional computing, making access to reliable power and cooling infrastructure paramount.
Power Infrastructure
AI data centers require substantially more power density than conventional facilities, often exceeding 50kW per rack compared to 5-10kW in traditional environments. Critical power components include:
- High-density power distribution units (PDUs) capable of delivering 400V+ power
- Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems with sufficient capacity for AI workload spikes
- Backup generators sized for extended outages and rapid load transitions
- Power monitoring systems with real-time analytics and predictive maintenance capabilities
Cooling Systems
Traditional air cooling proves inadequate for AI workloads. Modern AI data centers implement advanced cooling strategies:
- Liquid cooling solutions including direct-to-chip and immersion cooling
- Rear door heat exchangers for high-density rack configurations
- Free cooling systems leveraging external air temperatures when possible
- Precision cooling units with variable speed controls and intelligent airflow management
2. Computing Hardware Architecture
AI-Optimized Processors
The heart of AI data centers consists of specialized processing units designed for machine learning workloads:
Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) remain the dominant choice for AI training and inference, with modern cards like NVIDIA H100s and AMD MI300X providing exceptional parallel processing capabilities for neural network operations.
Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) offer Google’s custom silicon approach, optimized specifically for TensorFlow operations and providing superior energy efficiency for certain AI workloads.
Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) provide flexibility for custom AI algorithms and real-time inference applications requiring ultra-low latency.
AI-specific processors from companies like Intel (Habana), Cerebras, and GraphCore offer specialized architectures designed from the ground up for machine learning operations.
High-Performance Computing Infrastructure
AI workloads demand robust server architectures with:
- High-memory configurations supporting 1TB+ RAM per server for large model training
- NVMe storage arrays providing the IOPS necessary for data-intensive training pipelines
- Multi-GPU server designs enabling parallel processing across multiple accelerators
- Advanced cooling integration built directly into server chassis design
Storage Systems
AI data centers require sophisticated storage architectures to handle massive datasets:
High-performance parallel file systems like Lustre, GPFS, or WekaFS provide the throughput needed for training data access across distributed computing clusters.
Object storage systems offer cost-effective solutions for long-term dataset retention and model versioning.
All-flash arrays deliver the low-latency access patterns required for real-time inference workloads.
3. Networking Infrastructure
High-Bandwidth Interconnects
AI workloads generate enormous east-west traffic patterns requiring specialized networking:
InfiniBand networks provide ultra-low latency interconnects essential for distributed training across multiple nodes, with modern implementations delivering 400Gbps+ per port.
Ethernet fabrics using 100GbE and 400GbE links create cost-effective alternatives for less latency-sensitive workloads.
Specialized AI networking solutions like NVIDIA’s NVLink and NVSwitch enable direct GPU-to-GPU communication across server boundaries.
Network Architecture Design
Modern AI data centers implement spine-and-leaf architectures optimized for machine learning traffic patterns, with consideration for:
- East-west traffic optimization supporting model parameter synchronization
- Network congestion control preventing training slowdowns during gradient updates
- Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization for different AI workload types
- Software-defined networking (SDN) enabling dynamic resource allocation
4. Software Infrastructure Stack
Orchestration and Management Platforms
AI data centers require sophisticated software platforms for workload management:
Kubernetes serves as the foundation for container orchestration, with AI-specific distributions like NVIDIA’s DGX Cloud and Google’s GKE providing optimized environments for machine learning workloads.
Cluster management systems such as Slurm, PBS, or Kubernetes-based solutions handle resource scheduling and job queuing for training pipelines.
MLOps platforms integrate development, training, and deployment workflows, incorporating tools like MLflow, Kubeflow, or custom solutions.
AI Frameworks and Runtime Environment
The software stack must support diverse AI frameworks:
- Deep learning frameworks including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and JAX
- Runtime optimization through TensorRT, Apache TVM, or ONNX Runtime
- Distributed training libraries like Horovod, FairScale, or framework-native solutions
- Model serving platforms such as TorchServe, TensorFlow Serving, or Triton Inference Server
Data Management and Pipeline Tools
AI workloads require sophisticated data handling capabilities:
Data versioning systems track datasets across model development cycles, ensuring reproducibility and compliance requirements.
ETL/ELT pipelines process raw data into training-ready formats using tools like Apache Spark, Dask, or Ray.
Feature stores centralize feature engineering and serve real-time features for inference workloads.
5. Security and Compliance Framework
Data Protection
AI data centers must implement comprehensive security measures:
Encryption at rest and in transit protects sensitive training data and model parameters using hardware security modules and advanced encryption standards.
Access control systems implement zero-trust architectures with multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls.
Network segmentation isolates AI workloads and implements microsegmentation for lateral movement prevention.
Model and Intellectual Property Security
Protecting AI models and training data requires specialized approaches:
- Model encryption during storage and inference
- Secure multi-party computation for collaborative AI development
- Differential privacy techniques protecting individual data points
- Adversarial attack protection preventing model manipulation
Regulatory Compliance
Modern AI data centers must address evolving regulatory requirements:
- GDPR and data locality requirements for European operations
- Industry-specific regulations such as HIPAA for healthcare AI
- AI governance frameworks addressing model bias and explainability
- Export control compliance for advanced AI technologies
6. Monitoring and Operations
Performance Monitoring
AI workloads require specialized monitoring approaches:
GPU utilization tracking monitors accelerator efficiency and identifies bottlenecks in training pipelines.
Model performance metrics track accuracy, latency, and throughput across different workload types.
Resource utilization analysis optimizes cluster efficiency and identifies opportunities for workload consolidation.
Predictive Maintenance
AI data centers benefit from intelligent operations management:
- Thermal monitoring prevents overheating in high-density configurations
- Power consumption analytics optimize energy efficiency and predict capacity needs
- Component failure prediction using machine learning on operational telemetry
- Automated remediation systems respond to common operational issues
Capacity Planning
AI workload growth requires sophisticated planning:
Demand forecasting models predict future compute and storage requirements based on AI model development roadmaps.
Resource optimization algorithms maximize cluster utilization through intelligent workload placement.
Scalability planning ensures infrastructure can accommodate rapid AI adoption growth.
7. Economic and Sustainability Considerations
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
AI data centers require careful economic analysis:
Capital expenditure planning accounts for higher hardware costs and shorter refresh cycles compared to traditional data centers.
Operational expense optimization focuses on power efficiency and automated operations to control ongoing costs.
Workload economics analyze cost per training run and inference request to optimize pricing models.
Environmental Sustainability
Growing environmental concerns require sustainable AI infrastructure:
Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) optimization through advanced cooling and power management systems.
Renewable energy integration reduces carbon footprint through on-site generation and power purchase agreements.
Hardware lifecycle management maximizes equipment utilization and implements responsible disposal practices.
8. Emerging Technologies and Future Considerations
Next-Generation Hardware
The AI data center landscape continues evolving with emerging technologies:
Quantum computing integration may complement classical AI workloads for specific optimization problems.
Neuromorphic computing offers potential energy efficiency advantages for inference workloads.
Advanced packaging technologies like chiplet designs and 3D stacking increase performance density.
Edge AI Integration
Modern AI strategies require hybrid cloud-edge architectures:
- Edge inference deployment reduces latency for real-time applications
- Federated learning enables distributed model training across edge locations
- Model compression techniques optimize models for resource-constrained edge devices
Implementation Roadmap
Successfully implementing AI data center projects requires phased approaches:
Phase 1: Foundation (Months 1-6)
Establish basic infrastructure including power, cooling, and network backbone. Deploy initial compute clusters with standard hardware configurations.
Phase 2: Specialization (Months 6-12)
Integrate AI-specific hardware, implement advanced cooling solutions, and deploy ML orchestration platforms.
Phase 3: Optimization (Months 12-18)
Fine-tune performance, implement advanced monitoring, and optimize operational processes.
Phase 4: Scale (Months 18+)
Expand capacity based on demand patterns and integrate emerging technologies.
Conclusion
AI data centers represent a fundamental shift in computing infrastructure design, requiring specialized approaches across hardware, software, and operational domains. Success depends on understanding the unique requirements of AI workloads and implementing integrated solutions that address computational intensity, data movement patterns, and operational complexity.
Organizations planning AI data center investments should focus on flexible, scalable architectures that can adapt to rapidly evolving AI technologies while maintaining operational efficiency and cost effectiveness. The building blocks outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive framework for developing world-class AI computing infrastructure.
As AI continues transforming industries and society, the data centers supporting these workloads will become increasingly critical infrastructure. Thoughtful planning and implementation of these building blocks will determine the success of AI initiatives and competitive advantages in the digital economy.



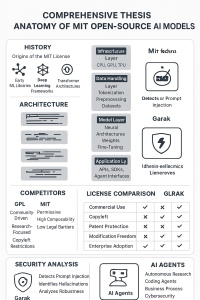
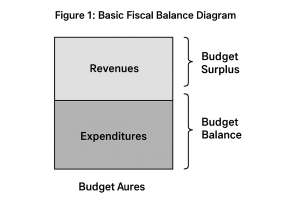
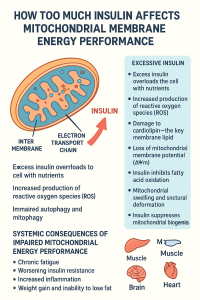
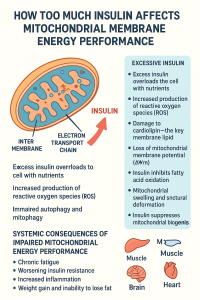
Be First to Comment